Overview
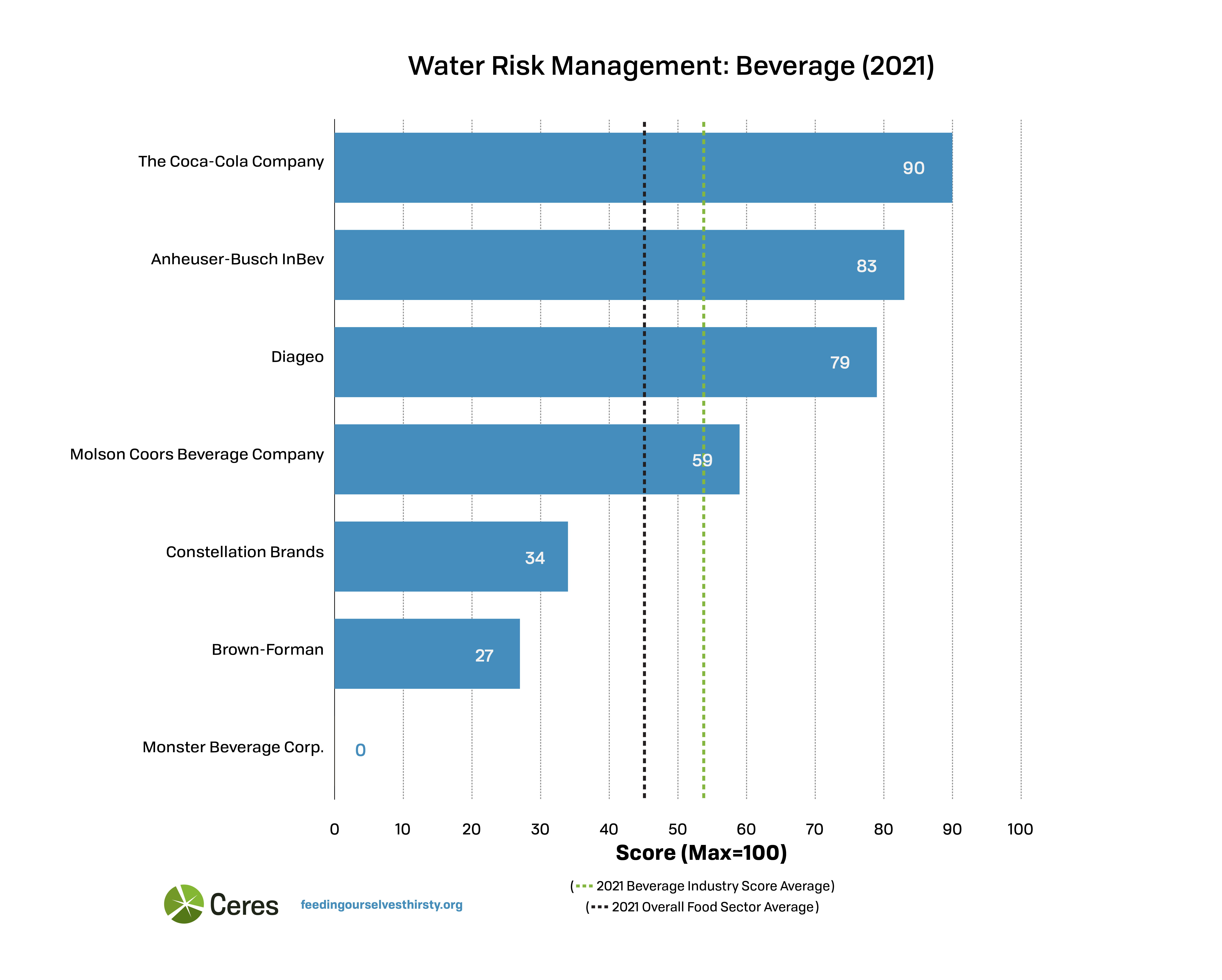
The Beverage industry, which has encountered significant reputational and license-to-operate risks associated with its water use, was the second highest performing industry, with an average score of 53 points out of 100. At the same time, corporate performance diverged widely, with Coca-Cola, Anheuser Busch InBev, and Diageo finishing in the top 10 overall, Constellation Brands and Brown-Forman in the bottom half, and Monster Beverage getting the lowest score, 0 points, of all 38 companies.
Only a selection of indicators are represented. See the scoring guidance here.
Areas of Strength
Governance
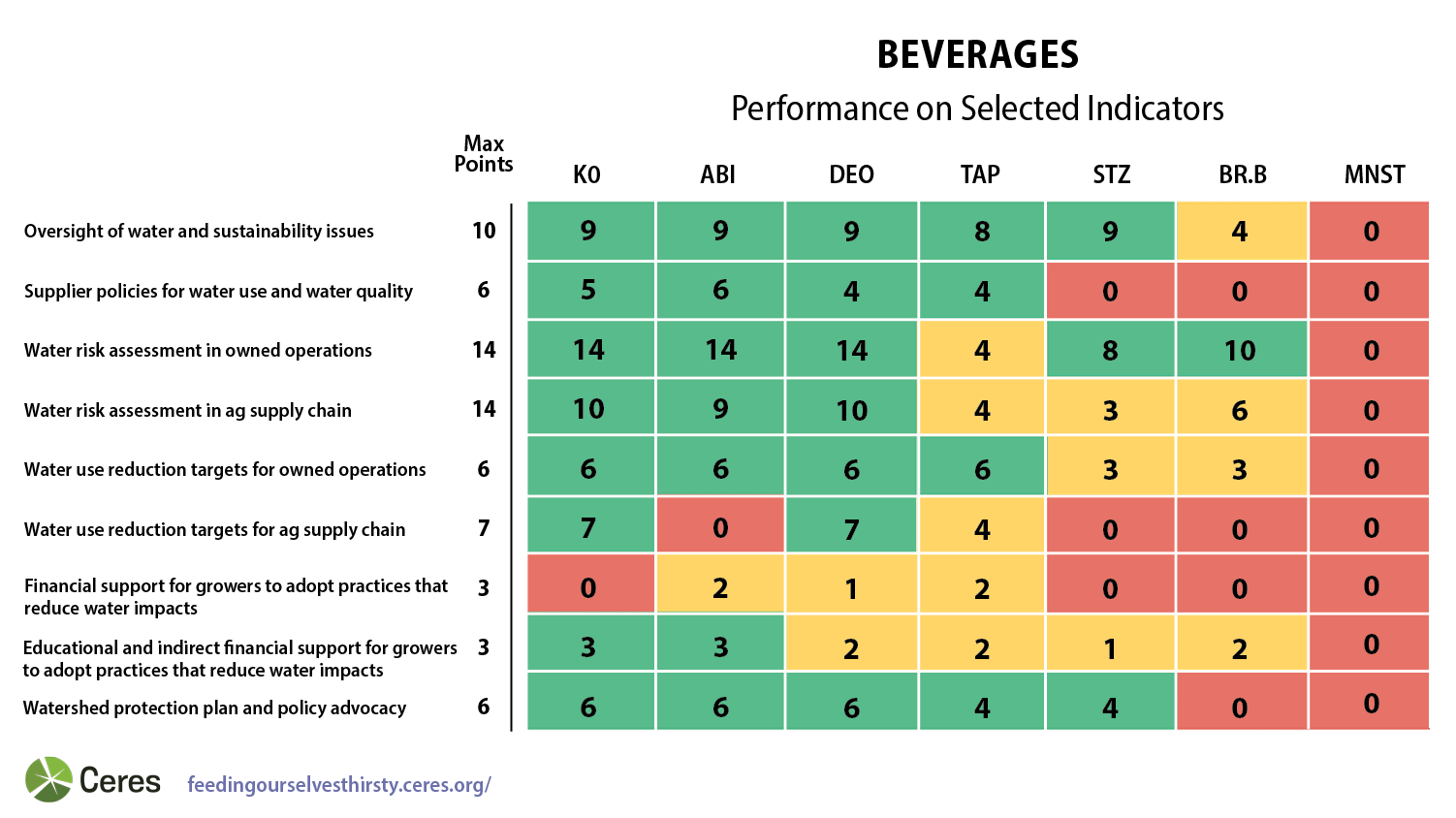
Nearly all of the companies have strong board oversight of sustainability issues and have established a senior-level position with direct oversight over water and a direct link to either the C-suite or senior management. Coca-Cola’s Public Policy and Sustainability Committee of its board of directors, which has the highest level of direct responsibility for water-related issues within the company, is recognized as a leading practice in the sector. In stark contrast, Monster Beverage and Brown-Forman have not implemented board level oversight of sustainability or water-related issues.
Risk assessment in direct operations
Nearly all beverage companies have conducted a water risk assessment in their owned operations that includes water quality. Most companies have also disclosed specific high risk watersheds and the quantity and percentage of water withdrawn and consumed from high risk regions. Anheuser Busch InBev, Coca-Cola, Brown-Forman, and Diageo all disclosed the volume and percentage of water they withdraw and consume from high risk regions.
Indirect Financial Incentives/Educational Support
All of the companies, except Monster Beverage, offer educational support for producers, a clear signal that they have prioritized supplier engagement on sustainable agriculture practices. Anheuser Busch InBev and Coca-Cola have taken it a step further by implementing supplier training programs in high risk watersheds. Three companies, Molson Coors, Anheuser Busch InBev, and Diageo, are providing direct financial incentives to producers, including programs that are directly connected to broader sustainable agriculture goals.
Collective Watershed Action
A considerable number - five - of the companies analyzed have developed a watershed protection plan for high risk regions, including initiatives such as water replenishment, water efficient crops, reforestation, and ecosystem restoration.
Areas for Improvement
Risk Assessments and Targets in Agricultural Supply Chain
Many beverage companies have not performed a water risk assessment of their agricultural supply chain that includes water quality. Even among those that do, no company has comprehensively disclosed high risk watersheds based on water quality and availability. There has also been weak disclosure regarding the percentage of agricultural products sourced from high risk watersheds. Brown-Forman, Diageo, and Coca-Cola were the only companies to fully disclose this.
While nearly all companies have implemented water use efficiency targets for their owned operations, there has been little progress in setting targets to reduce water pollution and only a handful have made commitments to reduce water use in their agricultural supply chains. Few companies have reported time-bound targets that promote sustainable sourcing practices in their agricultural supply chains.
Among the stronger performers are Diageo and Coca-Cola, which have both developed goals to reduce water use in their supply chains, including aggressive targets for water stressed regions.
Coca-Cola, in particular, has taken steps to set water-related targets across its entire value chain, from owned operations to its supply sheds and surrounding communities. These include goals to implement regenerative water use practices (reduce, reuse, recycle, and replenish) in 100% of its priority manufacturing locations by 2030.
Scaling Implementation
While many companies showed improvement in providing financial incentives and educational support to producers, companies should improve the way these incentives are targeted towards producers in high risk watersheds. Only one company, Anheuser Busch InBev, has provided direct financial support for suppliers in high risk basins.
Additionally, most companies have not implemented incentive programs that reach more than 50% of producers. Molson Coors is a peer leader in supplier engagement, having developed an incentive program that applies to 99% of its barley farmers, in alignment with its goal to sustainably source 100% of its barley and hops.
Scoring Guidance for Selected Indicators
| Oversight of water and sustainability issues (Total possible score = 10 points) | |
| 2 points |
Board or board committee has oversight over sustainability ( +1 point) OR Board or board committee has explicit oversight over water-related issues (+ 2 points) |
| 3 point | Board or board committee is regularly briefed by management on water related issues |
| 4 points |
The individual with the highest level of direct responsibility for water-related issues reports directly to a member of the Executive Management Committee (+ 3 points) OR The individual with the highest level of direct responsibility for water-related issues reports to the CEO (+ 4 points) |
| 1 points | Water is linked to pay or incentive compensation for senior executives implicitly or explicitly |
| Supplier policies for water use and water quality (Total possible score = 6 points) | |
| 3 points | Has a publicly available supplier policy outlining expectations for Tier 1 suppliers regarding water use and water quality that exceed regulatory compliance |
| 1 points | The policy has a clear requirement for agricultural suppliers to have a water use plan in high risk regions |
| 1 points | The policy has clear requirements for agricultural suppliers regarding water quality that exceed regulatory compliance in high risk regions |
| 1 points | The policy clearly defines protocols for non-compliance |
| Water risk assessment in owned operations (Total possible score = 14 points) | |
| 3 points | Discloses the percentage and volume of total water withdrawal from regions with high baseline water stress |
| 3 points | Discloses the percentage and volume of total water consumed from regions with high baseline water stress |
| 4 points | Analysis explicitly included risks associated with water quality |
| 4 points |
Analysis explicitly discloses high risk watersheds based on water quality (+ 2 points) AND/OR based on water availability (+ 2 points) |
| Water risk assessment in ag supply chain (Total possible score = 14 points) | |
| 6 points | Discloses the percentage of agricultural products sourced from regions with high baseline water stress |
| 4 points | Analysis explicitly included risks associated with water quality |
| 4 points |
Analysis explicitly discloses high risk watersheds based on water quality (+ 2 points) AND/OR based on water availability (+ 2 points) |
| Water use reduction targets for owned operations (Total possible score = 6 points) | |
| 3 points | Has time-bound water use reduction targets for direct operations |
| 3 points | Uses a risk-differentiated, context-based, or science-based approach, focusing on watersheds with high water stress |
| 3 points | Has targets to reduce water pollution impacts of its operational discharge, focusing on pollutants of concern |
| Water use reduction targets for ag supply chain (Total possible score = 7 points) | |
| 4 points | Has time-bound water use reduction targets for agricultural regions/commodities |
| 3 points | Uses a risk-differentiated, context-based approach, focusing on watersheds with high water stress |
| Financial support for growers to adopt practices that reduce water impacts (Total possible score = 3 points) | |
| 2 points | Provides financial incentives to producers to encourage adoption of practices that reduce impacts and dependence on water |
| 1 points | Identified in high-risk watershed specifically |
| Educational and indirect financial support for growers to adopt practices that reduce water impacts (Total possible score = 3 points) | |
| 2 points | Provides education or indirect financial incentives to producers to encourage adoption of practices that reduce impacts and dependence on water |
| 1 points | Identified in high-risk watershed specifically |
| Watershed protection plan and policy advocacy (Total possible score = 6 points) | |
| 4 points | Has developed a watershed protection plan or strategy for key watersheds identified as high risk in their agricultural supply chain which includes plans to support projects that improve conditions for the watershed in collaboration with key local stakeholders |
| 2 points | Consistently advocates for public policy action to protect water resources in company's priority watersheds |
Scores are based on companies' public disclosures as of June 15, 2021.



