Overview
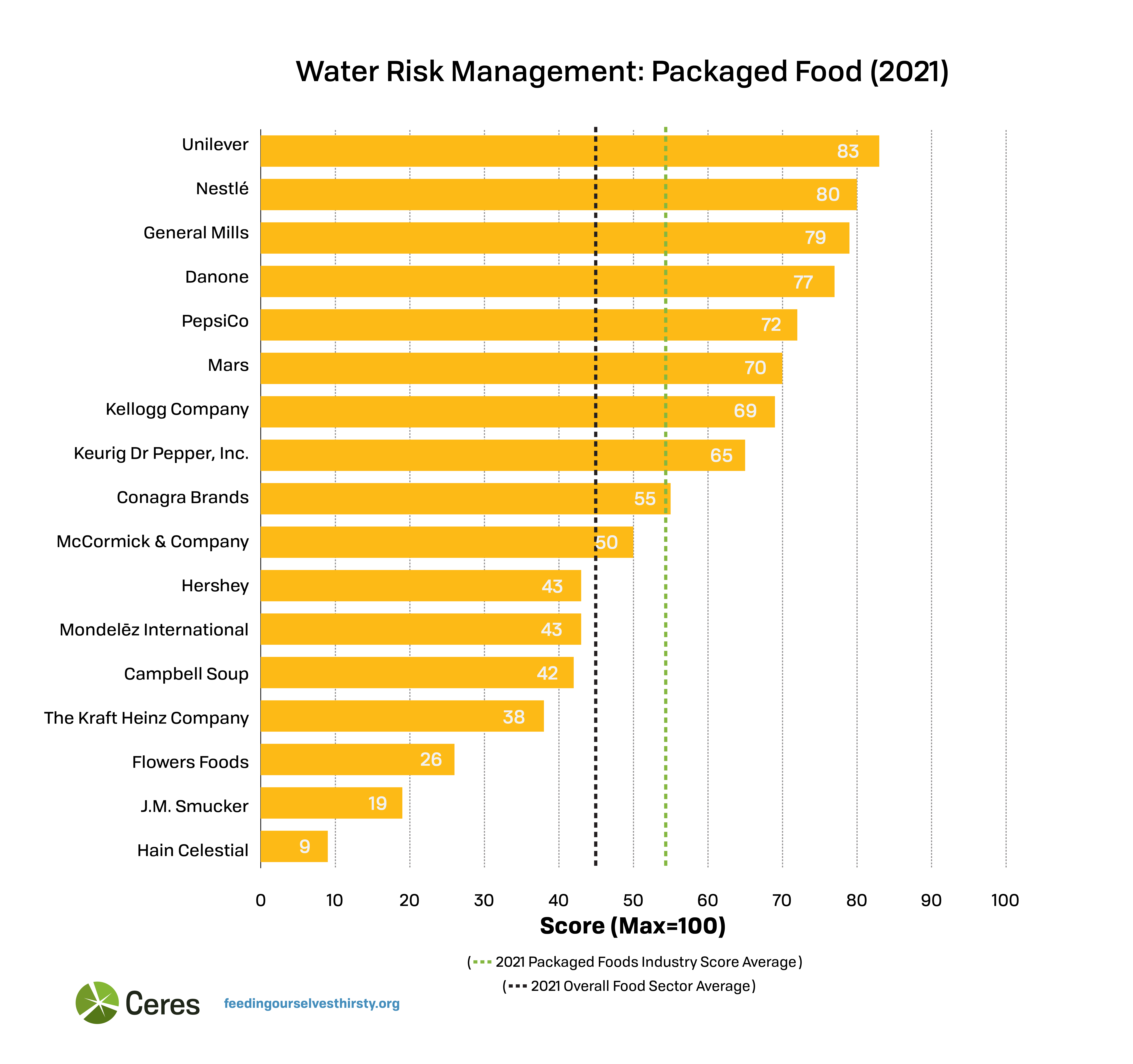
Companies in the Packaged Food industry must manage a diverse network of suppliers to grow and process the ingredients for their vast array of branded food products. Supply chain disruptions from physical water risks and consumer expectations for more sustainably produced products pose important risks and opportunities for these companies. The Packaged Food industry continued to be the highest performing group of companies, with an average score of 54 points. Six companies were top 10 performers, including Unilever, Nestlé, General Mills, PepsiCo, and Mars. This sector has the most impressive performance on governance indicators and water risk assessments.
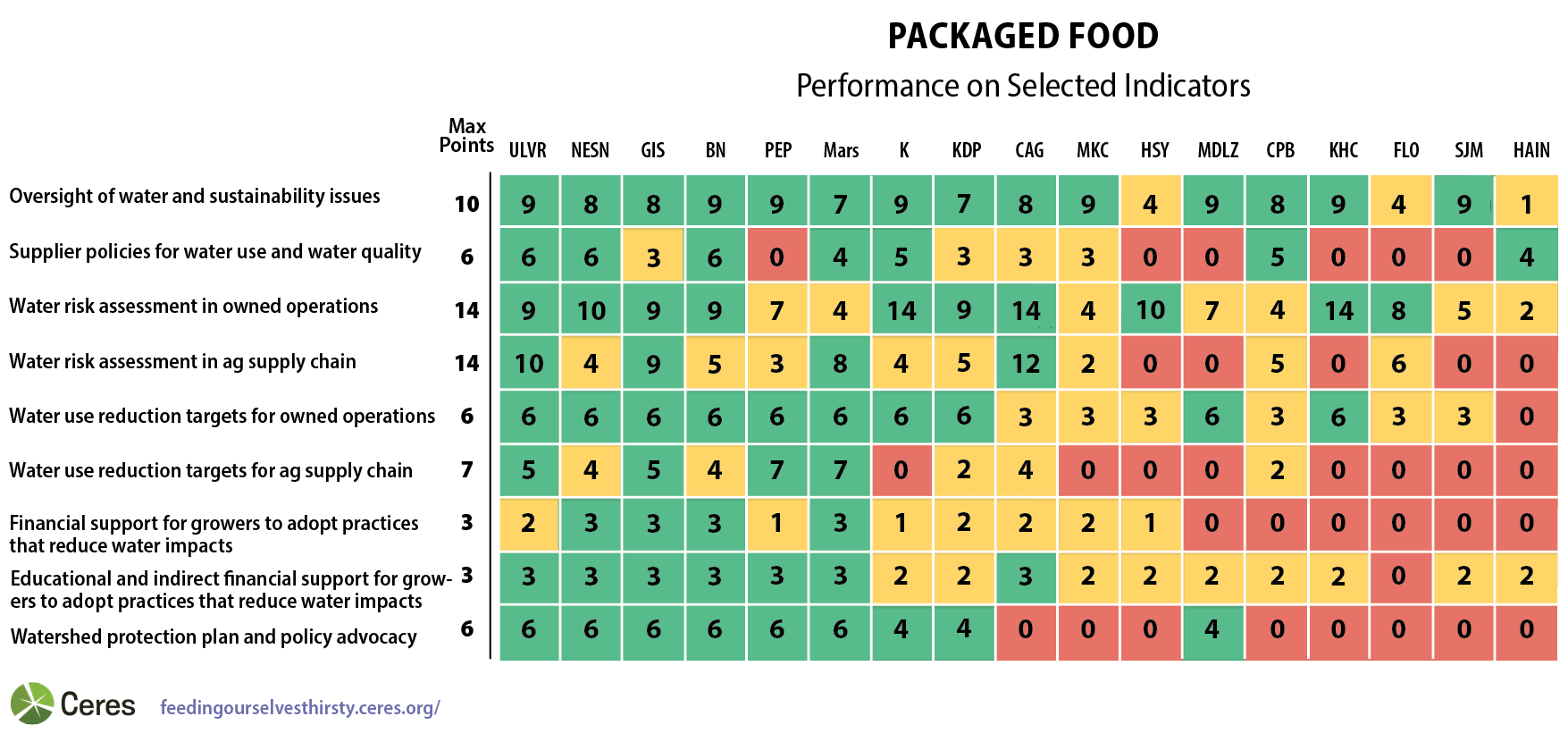
Only a selection of indicators are represented. See the scoring guidance here.
Areas of Strength
Governance
Nearly all of the companies have established strong governance structures for monitoring and improving water management, including board oversight over sustainability and senior executive oversight. Four companies have appointed their CEO as the individual with the highest responsibility for water strategies. More than half of the companies also link executive compensation to water-related objectives and have supplier policies with water-related objectives.
General Mills’ board has direct oversight over water-related issues and the Public Responsibility Committee assists the board on water stewardship topics. The Sustainability and Public Policy Committee on PepsiCo’s board has a key responsibility over water risks.
All 17 of the companies, except Hain Celestial, have established a senior management position with direct responsibility over water-related issues that reports directly to the C-suite or senior management. At PepsiCo, the CEO is a member of the Sustainability Subcommittee and the Risk Committee, making him directly in charge of managing water risks. Mars, Mondelez, and Kraft Heinz have also appointed their CEO as the individual with the highest level of responsibility over water issues.
Risk Assessment
This sector demonstrated the best performance of all industries, with nearly all companies, except J.M. Smucker and Flowers Foods, evaluating water conditions, including water quality risks, in their direct operations. They also have a good understanding of their agricultural supply chains, with more than half disclosing the percentage of commodities sourced from water-stressed regions.
General Mills has conducted a comprehensive water risk assessment for owned operations, assessing 20 key ingredients and 255 facilities. It has also assessed its water-related risks in growing regions and has published a map with high risk facilities identified by region, watershed, and the type of commodity sourced.
Kellogg’s has identified 20 owned facilities exposed to water risks and has disclosed total water consumption for all facilities.
J.M. Smucker’s weak water risk assessment performance contributed to its weak overall score.
Areas for Improvement
Supplier Policies
Few companies have disclosed a comprehensive supplier policy that includes expectations regarding water-related issues. Also, protocols for non-compliance have rarely been included in policy documents.
Agricultural Supply Chains
There is limited disclosure from this sector on agricultural products sourced from high risk regions and most have not performed water risk assessments for their supply chains that explicitly include water quality. There has also been limited action in providing financial incentives that apply to more than 50% of suppliers or suppliers in the high risk watersheds.
General Mills is a leading performer because it has disclosed a target to sustainably source 100% of its 10 priority commodities, while providing a detailed report on progress for each commodity.
Five companies, J.M. Smucker, McCormick, Kellogg’s, Mondelez, and Nestlé, were all downgraded in this indicator compared to 2019 due to our new expectation to report on the percentage of commodities sourced from water stressed regions.
Collective Watershed Action
While multiple companies disclosed examples of watershed protection efforts in the form of multi-stakeholder projects and public policy action, it is notable that less than half of this sector group received full credit for targeting such activities in regions identified as high risk.
Six companies have also disclosed examples of consistent public policy advocacy for water-related issues in areas such as regenerative agriculture and water stewardship; however, it is notable that 11 companies did not.
Financial Incentives
A small number of companies have provided financial incentives to farmers for promoting positive water outcomes. There is limited disclosure regarding programs that apply to more than 50% of suppliers or to suppliers in high risk watersheds.
Scoring Guidance for Selected Indicators
| Oversight of water and sustainability issues (Total possible score = 10 points) | |
| 2 points |
Board or board committee has oversight over sustainability ( +1 point) OR Board or board committee has explicit oversight over water-related issues (+ 2 points) |
| 3 point | Board or board committee is regularly briefed by management on water related issues |
| 4 points |
The individual with the highest level of direct responsibility for water-related issues reports directly to a member of the Executive Management Committee (+ 3 points) OR The individual with the highest level of direct responsibility for water-related issues reports to the CEO (+ 4 points) |
| 1 points | Water is linked to pay or incentive compensation for senior executives implicitly or explicitly |
| Supplier policies for water use and water quality (Total possible score = 6 points) | |
| 3 points | Has a publicly available supplier policy outlining expectations for Tier 1 suppliers regarding water use and water quality that exceed regulatory compliance |
| 1 points | The policy has a clear requirement for agricultural suppliers to have a water use plan in high risk regions |
| 1 points | The policy has clear requirements for agricultural suppliers regarding water quality that exceed regulatory compliance in high risk regions |
| 1 points | The policy clearly defines protocols for non-compliance |
| Water risk assessment in owned operations (Total possible score = 14 points) | |
| 3 points | Discloses the percentage and volume of total water withdrawal from regions with high baseline water stress |
| 3 points | Discloses the percentage and volume of total water consumed from regions with high baseline water stress |
| 4 points | Analysis explicitly included risks associated with water quality |
| 4 points |
Analysis explicitly discloses high risk watersheds based on water quality (+ 2 points) AND/OR based on water availability (+ 2 points) |
| Water risk assessment in ag supply chain (Total possible score = 14 points) | |
| 6 points | Discloses the percentage of agricultural products sourced from regions with high baseline water stress |
| 4 points | Analysis explicitly included risks associated with water quality |
| 4 points |
Analysis explicitly discloses high risk watersheds based on water quality (+ 2 points) AND/OR based on water availability (+ 2 points) |
| Water use reduction targets for owned operations (Total possible score = 6 points) | |
| 3 points | Has time-bound water use reduction targets for direct operations |
| 3 points | Uses a risk-differentiated, context-based, or science-based approach, focusing on watersheds with high water stress |
| 3 points | Has targets to reduce water pollution impacts of its operational discharge, focusing on pollutants of concern |
| Water use reduction targets for ag supply chain (Total possible score = 7 points) | |
| 4 points | Has time-bound water use reduction targets for agricultural regions/commodities |
| 3 points | Uses a risk-differentiated, context-based approach, focusing on watersheds with high water stress |
| Financial support for growers to adopt practices that reduce water impacts (Total possible score = 3 points) | |
| 2 points | Provides financial incentives to producers to encourage adoption of practices that reduce impacts and dependence on water |
| 1 points | Identified in high-risk watershed specifically |
| Educational and indirect financial support for growers to adopt practices that reduce water impacts (Total possible score = 3 points) | |
| 2 points | Provides education or indirect financial incentives to producers to encourage adoption of practices that reduce impacts and dependence on water |
| 1 points | Identified in high-risk watershed specifically |
| Watershed protection plan and policy advocacy (Total possible score = 6 points) | |
| 4 points | Has developed a watershed protection plan or strategy for key watersheds identified as high risk in their agricultural supply chain which includes plans to support projects that improve conditions for the watershed in collaboration with key local stakeholders |
| 2 points | Consistently advocates for public policy action to protect water resources in company's priority watersheds |
Scores are based on companies' public disclosures as of June 15, 2021.